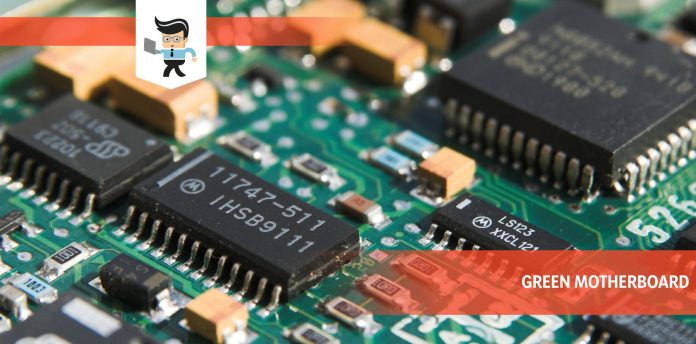
Most PC systems have a green motherboard since green is considered a conventional motherboard color, but there are other motherboard colors too.

In this detailed guide, we will explain why green is the most prevalent color in motherboard manufacturing and tell you all about other available colors for motherboards.
So if you’re asking yourself why your motherboard is a specific color, continue reading to find out!
Contents
Why Do I Have a Green Motherboard on My System?
Green is the most preferred color for the solder-resistant material placed on the outside layer of the circuit boards to make it easier to ensure that there are no migration of stray soldering material when soldering components.
The solder mask polymer is layered on top of the base material to insulate and protect the printed copper traces of a motherboard during the soldering process.
Initially, surface-mounted components on the motherboards were coated with drab brown hardened resins. This color was not appealing; for this reason, motherboard developers added green dye to the resin to make it more attractive.
With time, the solder green color was associated with Intel, a giant motherboard manufacturer. Their motherboards were predominantly green, and since they were producing quality devices, it boosted choosing the green color, especially for green gaming motherboards.
– Why Do Most Manufacturers Choose Green Solder Mask?
The base cost of green is less expensive than other colors, which is why it is widely used by manufacturers. Additionally, green is the only color that can reliably produce solder mask dams of 0.1mm.
Did you know that the frequency of the green light is less straining to the eye? Green color, according to optical specialists, minimizes eye strain. This makes it easier to differentiate various components on the motherboard. Therefore, screen printers/technicians find working with a green epoxy coating easier and more efficient.
For example, Silkscreen printing is easily legible on a green background. The extensive adoption of green as a standard color enables developers to use other colors of solder masks for prototypes.
Can I Find a Motherboard in a Different Color?
Yes, modern-day motherboards come in different colors such as yellow, red, and blue. These colors help to differentiate one brand from another or to showcase premium motherboards over standard ones.
Clear computer cases and case windows are quickly gaining traction, so the inner works are no longer hidden. With this in mind, developers try experimenting with different solder mask colors that give their products a distinctive appearance.
Here are the standard motherboard colors you will come across.
– Red
Red motherboards are popular now, unlike when they were used for testing purposes. The color contrasts the motherboard and its components more than most other colors. Ideally, the screen-printed white labels will stand out well on the red background.
These motherboards are most loved by gamers thanks to their vividness and brightness. Most support RGB, allowing you to mix different colors to create the best possible gaming experience. To most PC users, red motherboards symbolize power, passion, and intensity. For this reason, they are becoming a popular option, especially among gamers.
While good, the contrast and visibility for inspecting components on the red color are still not considered as good as green. Thus, it is not accepted as a superior color for contrast.
– Blue
Blue motherboards are attention-grabbing; thus, most developers use blue colors to make their products distinctive. The color offers a definite contrast between the screen-printed labels and the blue solder mask, so the blue solder mask can be a reasonable choice if a motherboard has many labels.
Blue motherboards are usually associated with devices and computers running on Windows 10 or 11 operating systems. The color shows support for Microsoft products, but different brands and models have embraced these motherboards.
However, blue does not provide the same contrast ability as green and red. Therefore, you may need to use magnifying instruments when inspecting the board traces.
– White
White is the least practical color choice for motherboards compared to other solder mask colors because it offers very little contrast. This can make it very difficult to inspect and clean the motherboard.
Nevertheless, the silkscreened labels do work effectively on the white background. Since few companies produce white motherboards, these motherboards are the most expensive.
– Black
The only good thing about black motherboards is the contrast. The silkscreening labels and the background contrast are clear and easily discernable. So, why are motherboards black? Motherboards are black to allow customization, but such PCBs sometimes represent the ability to overclock or intense gaming performance.
In essence, the black color is associated with high usability and performance. Otherwise, these motherboards are very difficult to work with. For starters, viewing and tracing component connections can be very difficult. You will need magnifying instruments and a specific light angle for proper viewing.
Additionally, black motherboards tend to absorb a lot of heat. This can cause the internal components to heat up, leading to malfunctioning. The cleaning process of the black motherboards is somewhat unique as it must go through a separate cleaning step to ensure that all residues are removed.
– Other Possible Colors
Purple, yellow, orange, and lime are other possible motherboard colors. The success of these motherboards has been varying due to different reasons. Consumers select these colors for aesthetics, especially if they buy computer towers with clear cases.
The availability of these motherboards is limited. Yellow motherboards have contrast levels similar to that of green and red. However, they are not a popular option among consumers. Thus, they have failed to establish a niche in the mainstream market. This could probably be because yellow is not as appealing as green and red.
Does a Motherboard’s Color Affect Its Performance?
No, a motherboard’s color is purely for aesthetics; therefore, it does not impact its performance. So whether you choose a red, green, black, or yellow motherboard, the performance of that system board depends on the hardware components.
The idea of developers to use flashy colors is to make the mainboard more attractive or distinctive in see-through towers. So if you are going for a build that looks pretty, get a matching color scheme motherboard. You will still see it even with all the components plugged in.
You will find color coding on different components attached to the motherboard, such as the RAM slots, but these colors only show the matching slots to use if you plan to install dual-channel memory in your system.
Can You Paint Your Motherboard?
Yes, you can paint your motherboard, but you must adhere to safety precautions to prevent the destruction of essential components on the board. You will need to use 100 percent non-electrically conductive paint.
Nonconductive paint is the best paint for thermal and electric insulators as they protect systems and surfaces from overheating and short-circuiting.
Typically, paint without metal flakes or metallic finish can be an excellent nonconductive paint. The standard categories of nonconductive pains include Polymer coatings, Epoxy resin coatings, Phosphate coating, and Ceramic plasma sprayed coatings.
Each paint has its advantages and disadvantages, so be sure to select a paint that works for you. In addition, ensure that the paint does not get into any connectors, chips, pins, or plugs, such as the CPU socket, so you will need to cover them.
If you want to paint your motherboard, follow the procedure below:
– Step 1: Preparation
In this initial step, you will need all the necessary instruments that you will need to paint your circuit board. Ideally, you will need the following:
- Masking tape / Painter’s tape
- Flathead Jewelers screwdriver
- Blade / Scissors
Additionally, you will need to remove any components that you don’t need to be painted. This includes RAM, heatsinks, fans, and cards (PCI or AGP). Cover open floppy connectors, memory slots, and IDE using masking tape. Do the same for I/O plugs.
Also, wrap the connection pins with masking tape to prevent them from getting painted. Although not necessary, you can remove stickers to improve the finished look. Finally, use a paintbrush to remove any remaining stuff. Ensure that there are very few materials left on the motherboard.
– Step 2: The Actual Painting
With all essential surfaces covered, you can now start the painting process. Just ensure that you have non-conducting spray paint of the right color. Again, if you want to have a multicolored scheme, buy different colors.
Place the motherboard on a plain surface where you will be painting.
- Shake your paint vigorously, which ensures that it’s consistent. Now, you will need to spray away from the board and then spray over the board. Do not stop painting until you are pointing away from the board. That will prevent ugly splotches on the board.
- Let the paint stand for a few minutes, and then assess your board for areas that need additional paint. After that, add another layer of paint. You will need to be a professional painter to get the best paint.
Reminder: Painting your motherboard is not a good idea. If you want to change the color, buy a new motherboard of the desired color instead. Alternatively, you can purchase motherboard covers and paint them.
Can You Buy a Customized Color Motherboard?
Yes, you can buy a customizable motherboard. For instance, NZXT has designed the N7 motherboard, which allows you to alter the color scheme with an assortment of heatsink covers, available in glossy red, blue, or purple to match its cases.

Additionally, the manufacturer offers two metal motherboard covers, one in black and one in white. This results in a more colorful motherboard without the dependence on RGB lighting. Alternatively, you can customize your motherboard’s color from Printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturers.
A PCB is a blank circuit board, i.e., it does not have any electronic components attached to it. Since it does not have electrical components, it is not yet functional. Since they allow for customization, they come at a relatively higher price.
So if you are willing to spend more, you can order such motherboards. PCB companies specially design these motherboards for specific use. This gives flexibility to those needing to customize the look of their system’s motherboard.
What’s the Best Solder Mask Color for Motherboards?
Green solder mask is the most predominant color on motherboards today. While there is no clear consensus on why green is the most common color used in the soldering process, there are attributes that support its use.
- A green solder mask can be used to develop the smallest solder mask dams (0.1 mm). Blue, yellow and red can generate dams of 0.12 mm, while white and black, which provide the greatest contrast for silkscreen, create 0.15 mm solder mask dams.
- Green light has a wavelength of approximately 550 nm. This makes it the most visible color to human light in daylight.
Color is one of the multiple considerations influencing the type of solder mask used. However, the major consideration is the type of system in which you plan to deploy the board. Boards destined for use in certain industries or specific applications must adhere to the standards outlined in IPC-SM-840D.
– What Is the Motherboard Solder Mask?
A solder mask is a thin lacquer-like layer of polymer applied to traces of copper on a PCB or motherboard to protect it against oxidation. The solder mask layer is also necessary to prevent solder bridges from forming between closely placed solder pads.
This substance is also called solder stop mask, solder resists, or solder green oil, and typically, the principal protection against oxidation and corrosion. It guards against performance degradation and extends the device’s normal operational lifetime.
The primary solder mask medium is resin, thanks to its unique qualities such as better insulating properties, solder resistance, humidity resistance, and temperature resistance. Other materials used to make medium include plastic, metal, and Bakelite.
Soldering, connecting two pieces of metal with hot, molten solder, typically creates sparks. These sparks can damage your motherboard’s components. The solder mask on the motherboard allows safe connection by preventing sparks or heat from contracting the motherboard. Additionally, the solder mask protects the components from solder flux.
– Purposes of Solder Mask
The solder mask greatly affects the quality of the board. Here are the most common impacts of solder masks:
- Prevention of solder bridges: The solder mask provides a solder dam between solder joints alongside other conductive areas of the motherboard where solder bridges may form, potentially leading to board damage or short circuits.
- It reduces solder paste consumption during the soldering process.
- It offers additional insulation of the components from the PCB as it serves as extra insulation of the PCB components.
- It protects against contaminants introduced while handling the board. Additionally, it prevents the oxidation process, which may shorten the operational life of the computer.
- The solder mask may increase the breakdown voltage of the motherboard’s dielectric material, providing additional protection against arcs typically associated with high voltage (above 1 kV) boards.
- It helps to avert the growth of tin whiskers, primarily associated with lead-free solder or tin-plating for electronic components.
The solder mask is essential to your board’s operation once deployed. Nevertheless, there are situations where it may not be possible or desirable to have a solder mask, for instance, small components and fine pitches on ball grid arrays (BGAs).
But before you decide to forego the solder masks for design alternatives, you should ensure there are no adverse effects on your board’s performance or reliability.
– Installing Solder Mask on a Motherboard
Follow the steps below to apply a solder mask on a motherboard:
- Board cleaning: Clean the board to remove dirt and other contaminants. Dry the board afterward.
- Apply ink coating: Coat the motherboard with liquid ink coating. Usually, the board is loaded into a vertical coater. You can customize the thickness of the layer based on reliability and functionality. Different parts of the motherboard have different thicknesses, so pay attention to this detail.
- Pre-hardening: This stage aims to make the coating relatively solid to easily remove the excess/unwanted oil without damaging the motherboard.
- Imaging and Hardening: Imaging is achieved using laser-plotted photo film to define the solder mask area. The film is aligned to the panel already solder inked and tracked dried. The film is then subjected to UV, causing the ink below to polymerize or harden.
- Development state: In this stage, place the board in a developer to remove the unwanted solder mask. This ensures that the required copper foil is accurately exposed.
- Final hardening and cleaning: This stage makes the solder ink mask available when mounted on the PCB surface. You may further clean them to make them usable, for instance, by applying a surface finish.
FAQs
– What Is the Role of a Motherboard in a PC?
A motherboard is a PCB that holds modular devices and facilitates communication among devices to facilitate proper computer functioning. Devices such as Hard disk, RAM, and CPU, initially connect to the motherboard.
The specific roles of a motherboard include:
- Power Distribution: The motherboard is also responsible for distributing power to the various components of the computer.
- Data Flow: The motherboard is a communication hub for all the connected peripherals. All peripherals communicate or send/receive data through the motherboard, which manages the data traffic.
- Component’s Hub: The motherboard acts as the central backbone of a PC on which other modular components are placed, such as the CPU, RAM, and hard disks.
- Slots for External Peripherals: The motherboard is the platform on which different expansion slots are available to install other interfaces.
- BIOS: The motherboard holds Read Only Memory, BIOS, which is required to boot up the computer. Thus, the motherboard plays a role in starting the computer.
– Motherboard vs. Circuit Boards: What Is the Difference?
The main difference between a motherboard and a circuit board is that the motherboard is the system unit’s main board that links different peripherals of a computer, while a circuit board acts as the pathway for the electrical and data transfer of different elements connected to it.
Motherboards allow the different parts of the computer to communicate with each other efficiently, leading to a seamless performance. Motherboards are simply circuit boards, but not all circuit boards are motherboards. The motherboard allows users to add other circuit boards through expansion ports, slots, and connection points.
The circuit board may be highly specialized to perform specific tasks or be designed to provide many functionalities.
– Should I Get an Armor for My Motherboard?
The decision to buy a motherboard armor or cover plate is entirely optional. However, most top-end motherboards come with cover plates. The primary role of the cover plate is to protect the components installed on the motherboard and help keep the motherboard cooler.
If your motherboard does not have armor, it might not be easy to install one due to incompatibilities. While some manufacturers, such as NZXT, offer customizable armor to match the color scheme of your computer, they still may not fit on your motherboard.
But if you have the technical know-how, you can design a homemade DIY motherboard cover. In this case, you will need acrylic and Plexiglas. Also, you can paint them to fit your motherboard’s color scheme.
Cover plates have shortcomings, including reduced access to the motherboard components. For instance, when you need to change the CMOS batter, you must remove the whole motherboard armor.
Conclusion
We have described the motherboard color meaning in detail.
Here is a summary of the most important points we discussed in the guide above:
- Standard motherboard colors are green, yellow, blue, black, and red, but the most common motherboard color is green.
- The resin applied on the motherboard influences the final color, and it can be used to differentiate between brands or performance.
- The motherboard color does not influence performance but is purely for aesthetics.
- You can easily buy a customized motherboard in your favorite color.
If you are wondering why most motherboards are green, we have given you the complete details in this guide. Use the information to your benefit, and get the color of your choice today!