If you’re browsing about the CAS latency 16 vs 18 for your gaming setup, then you’re probably out here to find a comprehensive guide on the topic. In the guide below, we will be discussing many aspects that affect CAS latency and will also compare these effects on both types of RAM.
 Also included are recommendations about which type of CAS latency will be good for you, so make sure to thoroughly read the full article!
Also included are recommendations about which type of CAS latency will be good for you, so make sure to thoroughly read the full article!
Contents
CAS Latency 16 vs 18 Comparison Table
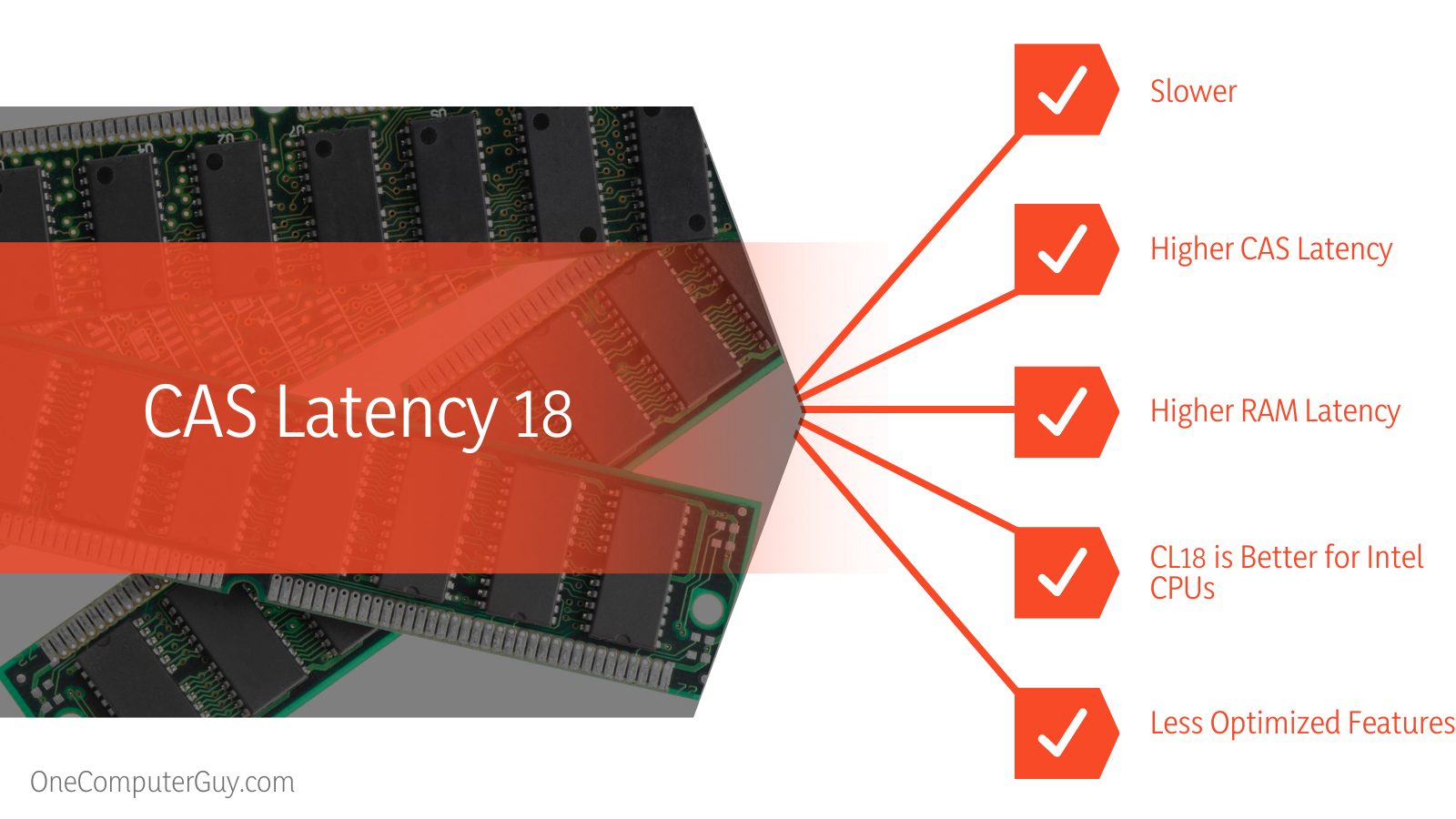
| Factor | CAS Latency 16 | CAS Latency 18 |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| CAS Latency | Lower | Higher |
| RAM Latency | Lower | Higher |
| CPUs | CL16 is better for AMD CPUs | CL18 is better for Intel CPUs |
| Features | More optimized | Less optimized |
What Are the Differences Between CAS Latency 16 vs 18?
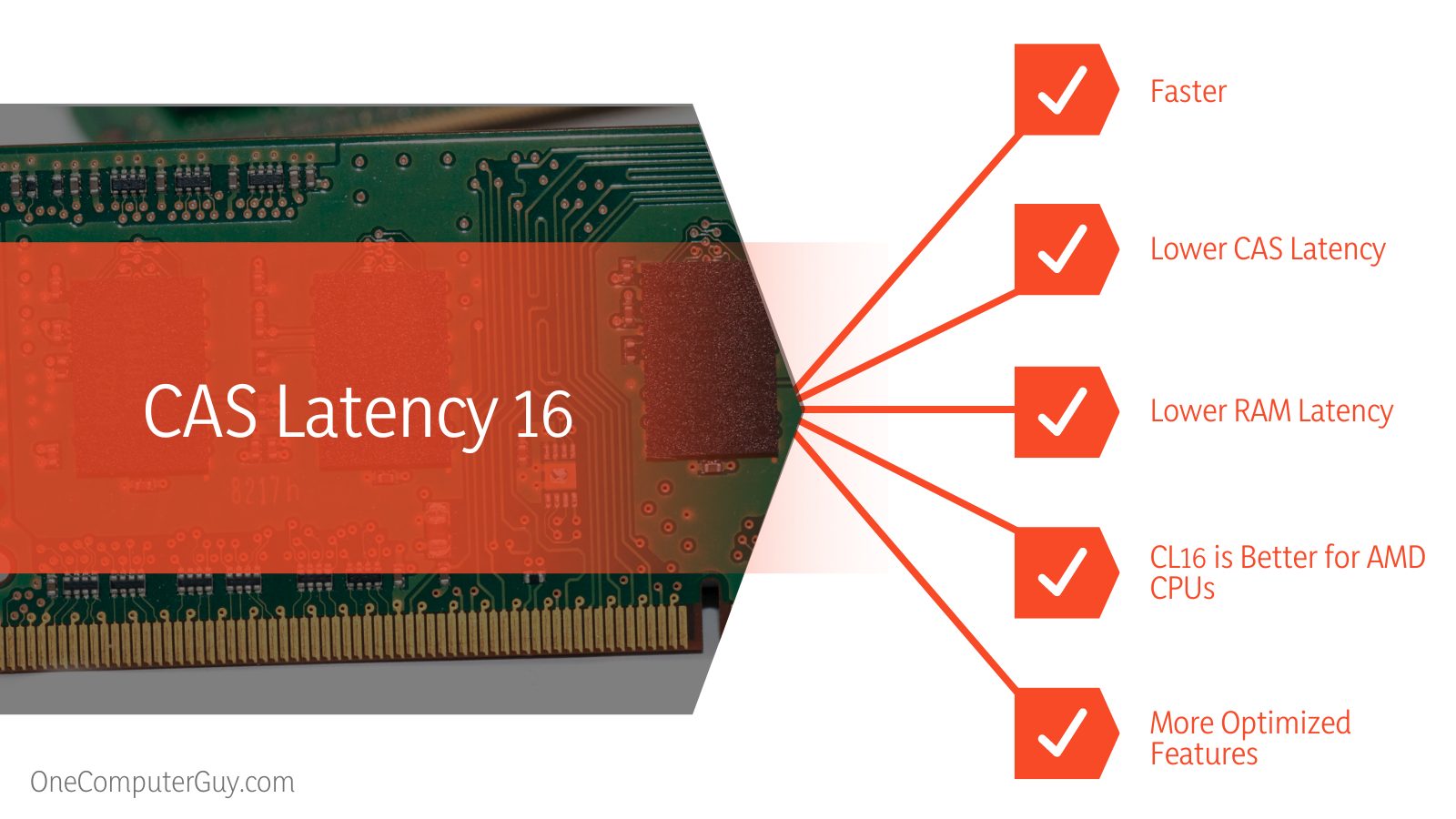
The main difference between CAS latency 16 vs 18 is that the CL16-rated RAM is more optimized and faces less latency as compared to a CL18-rated RAM. However, the CL16 rating also comes with an increase in costs. The CL18-rated RAMs are still pretty good for general usage.
– CAS Latency
Column Access Strobe Latency is referred to as CAS Latency. It describes the speed at which your RAM can prepare data in response to commands from your CPU. Let’s talk about it in greater depth.
 CAS Latency is the number of clock cycles needed by your RAM to carry out a CPU request. The RAM indicates the time delay in clock cycle periods when it tries to get data from the computer’s memory column.
CAS Latency is the number of clock cycles needed by your RAM to carry out a CPU request. The RAM indicates the time delay in clock cycle periods when it tries to get data from the computer’s memory column.
Boadly speaking, The amount of clock cycles required by a RAM module to access a specific piece of data in one of its columns and make that data available on its output is known as the CAS, or signal latency.
CAS delay can now be defined in a number of different ways. For example, a RAM stick with a CAS latency of 16 may be referred to as CAS 16 or CL16, or it may even say that it contains CAS 16 timings.
Lower CAS latency equates to faster performance regardless of memory speed. As a result, look for RAM modules with a relatively low Column Access Strobe Latency when searching for a RAM module with improved performance.
CAS timings and data transfer rates are frequently misunderstood. It’s crucial to keep in mind, though, that these two can vary for RAMs. When two RAM kits are sent at the same rate, the CAS timings frequently fluctuate.
– Speed
RAMs’ CAS latency or CL range varies as their speed changes. The rate at which a RAM accesses its memory is measured in terms of clock speed and expressed in the Megahertz (MHz) unit.
By checking the manufacturer’s website or your RAM stick, you can determine the CAS latency of your RAM. Your CAS delay is commonly represented by a series of three or four digits on the RAM stick. The speed of the RAM is the first point that we’ll compare between CAS latency 16 vs 18 RAMs.
– RAM Speed
RAM speed is a complicated subject. Although you might believe that RAM speed is solely influenced by clock speed, there are actually numerous more factors at play in determining RAM speed. The first and most frequently discussed feature of RAM speed is the data transmission rate.
This is the amount of information that a RAM and its CPU can send and receive at once. However, you must simultaneously look at your RAM’s clock speed and CAS latency to get a genuine sense of how quick it is.
Don’t worry if that felt a bit strange to read; we’ll take an example to try and understand this in the context of our CAS latency 16 vs 18 comparisons. In the case of a 3200 MHz RAM, a CL range of 14–16 is normal, whereas, for a 3600 MHz RAM, a CL range of 15–19 is typical. The former has a wider range than the latter, which lags.
This means that a 3200 MHz RAM with CL14 will operate better than a CL18 3600 MHz RAM despite having a faster memory speed. Thus, maintain your CAS latency as low as you can if you want to get the most out of your machine. In simple words, the lower the CAS latency number, the faster your RAM will be.
– RAM
As was already said, RAM latency, which is influenced by RAM speed, is the time it takes for the memory to finish a clock cycle. Faster performance is achieved by lowering RAM latency, which is achieved by increasing RAM speed.
We won’t get into this topic in detail because it is rather complex, but while reading RAM specifications, you’ll see numbers organized like 6-8-8-22. These four numbers show how long specific tasks in the RAM take to complete.
Overall, the faster the RAM, the lower these numbers should be, and this is the same in the case of CAS latency 16 vs 18. If you wish to comprehend their impact on the overall performance of RAM, a complete comprehension of both of these concepts is necessary.
– RAM Latency
Reduced RAM latency is the result of faster RAM, which enables your RAM to access memory more frequently and with shorter intercycle intervals. Additionally, RAM with a lower CL rating than RAM with a higher CL rating can complete the task in fewer cycles. For the sake of comprehension, let’s use the same example as earlier.
A CL16 RAM with 3600MHz will perform significantly more quickly than a CL18 RAM at 3200MHz. The latency of CL16 and CL18 is hence comparable, with CL18 being a little slower. Since a CL18 RAM requires two fewer cycles to accomplish the work than a CL16 RAM, you may process data faster with a CL16 RAM.
However, the difference between CL18 and CL16 would be less obvious than if there were a smaller margin, like a CL 16 and a CL 18 RAM that are both at 3600MHz.
 – CPUs
– CPUs
Generally speaking, compared to their Intel Core counterparts, Ryzen CPUs have proven to be more sensitive to RAM speed. These CPUs typically have faster memory access times. The total RAM performance of a Ryzen-based processor might not be up to par though, despite that. The clock time characteristics of the CPU core and AMD Ryzen chips differ from one another.
The FCLK clock cycle, which belongs to this system, has a maximum clock speed of 1800–2000 MHz. This FCLK can function at its best when the memory speed is two times the clock cycle.
Additionally, this directly affects the latency time of the infinite fabric system. Making the most of Ryzen, therefore, requires reducing the number of processes needed to execute a command. Therefore, if your CPU is a Ryzen model, you may largely ignore clock speed and concentrate on a lower CL. We advise deciding on the CL16 rather than the CL18.
– Processors
Going with the CL18 won’t be a bad choice, though, if you don’t mind the tiny 1 percent difference that just affects gaming PC performance. The situation in Intel CPUs is the polar opposite of what we observed in AMD processors.
When the memory clock time in Intel processors is so closely synchronized, things don’t happen. Consequently, you can maximize the performance of your processor by using quicker RAM.
Using a 3600 MHz CL18 and changing it to CL16 will work much better on PCs with Intel processors. On the other hand, a 3200 MHz CL16 RAM can run at its peak levels, but the latency is barely perceptible unless you require an extreme level of smooth gaming. In light of this, the CL18 with the higher frequency speed is the better choice when choosing CAS latency 16 vs 18 gaming.
– RAM Speed vs Latency RAM
You might be wondering what exactly is the distinction between the speed and latency of a RAM now that we have discussed both of them. In simple terms, the clock speed of a RAM, which determines how frequently it may access its memory per second, is measured as the RAM speed.
This means that a RAM running at 3200 MHz can access its memory 3200 times per second, whereas a RAM running at 3600 MHz can do so 3600 times per second.
The performance of the RAM is improved when the memory speed is higher. The RAM speed determines RAM latency, which is the amount of time the memory requires to finish a clock cycle. Lower RAM memory latency and faster performance are obtained with greater RAM speeds.
– Features
In the sections above, we’ve compared the most important aspects of the CAS latency 16 vs 18 comparison; but we haven’t really touched upon the features of CAS latency. If you compare the GPU usage percentages of both CL 16 and CL 18 RAMs, you’ll find that the percentage will be almost the same in both cases.
This same phenomenon also occurs in the case of GPU temperatures, CPU usage percentage, FPS, etc. In each of these cases, the measurement of CL16 RAM will be nearly identical to the CL18 RAM.
However, there are cases where the values for both CL 16 and CL 18 differ. For example, the VRAM used by CL 16 is higher than that used by CL 18 RAM.
You’ll find the same situation if you measure the RAM used by both types of CAS latency. We can safely say that the CL16 RAM is more optimized than a CL18 RAM stick. This leads to a higher demand for CL 16 RAM and, consequently, a higher cost for that RAM.
As a further plus point, CL18 RAMs tend to be less costly, too, so you don’t need to watch your purse too much if you want to get one.
What Is CAS Latency 16 Best For?
CAS latency 16 is best for allowing you to work while facing the lowest feasible latency. Having a CAS latency of 16 is of much importance to professional gamers and the like, who tend to milk their computers as much as possible and thus need to be mindful of such facts.
What Is CAS Latency 18 Best For?
CAS latency 18 is best for casual PC users. If you are a regular person and aren’t involved in any competitive e-sports, it’s possible that you might not even feel the difference in the speed between CL16 and CL18 RAMs.
Conclusion
As a conclusion to this CAS latency 16 vs 18 comparison, we’d like to further reiterate the fact that for casual or business users, having a CL18 RAM or a CL16 RAM will not make much of a difference.
However, if you are a pro gamer, then we’d recommend you to get a RAM with a CL16 rating. These RAMs are more optimized than the CL18 ones and will make sure you face the least amount of latency possible with a RAM of this rating.







