Choosing between NAT vs bridged as the computer networking mode is never easy, especially in terms of creating a secure connection or data sharing for accessibility.
 However, this does not mean both options can be used always.
However, this does not mean both options can be used always.
There are differences between them that you must know before you make your pick, and so this article will explain which option is best for you!
Contents
- NAT vs Bridged Comparison Table
- What Is The Difference Between NAT and Bridged?
- What Is NAT Connection Best For?
- What Is Bridged Mode Best For?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- – How Does The Bridged Connection Work?
- – How Does The NAT Connection Work?
- – What Are The Differences Between Nat vs Bridged Mode With Regards to Connection?
- – Is Nat Preferable to Bridge?
- – When Should You Use Bridged Mode?
- – Is NAT Effective For Security Purposes?
- – Is Bridged Mode Expensive?
- – Is NAT A Simple Network?
- Conclusion
NAT vs Bridged Comparison Table
| NAT Connection | Bridged Connection |
| Virtual Machine will be assigned to a separate subnet | Virtual Machine will be on a similar network as your host |
| Nat shares the host’s network connection by assigning a private network IP address to the router or Virtualbox nat and translating network requests from the guest. | The host shares its physical adapters with a “Bridged” network adapter, which means the adapter joins the network configuration like any other physical system. |
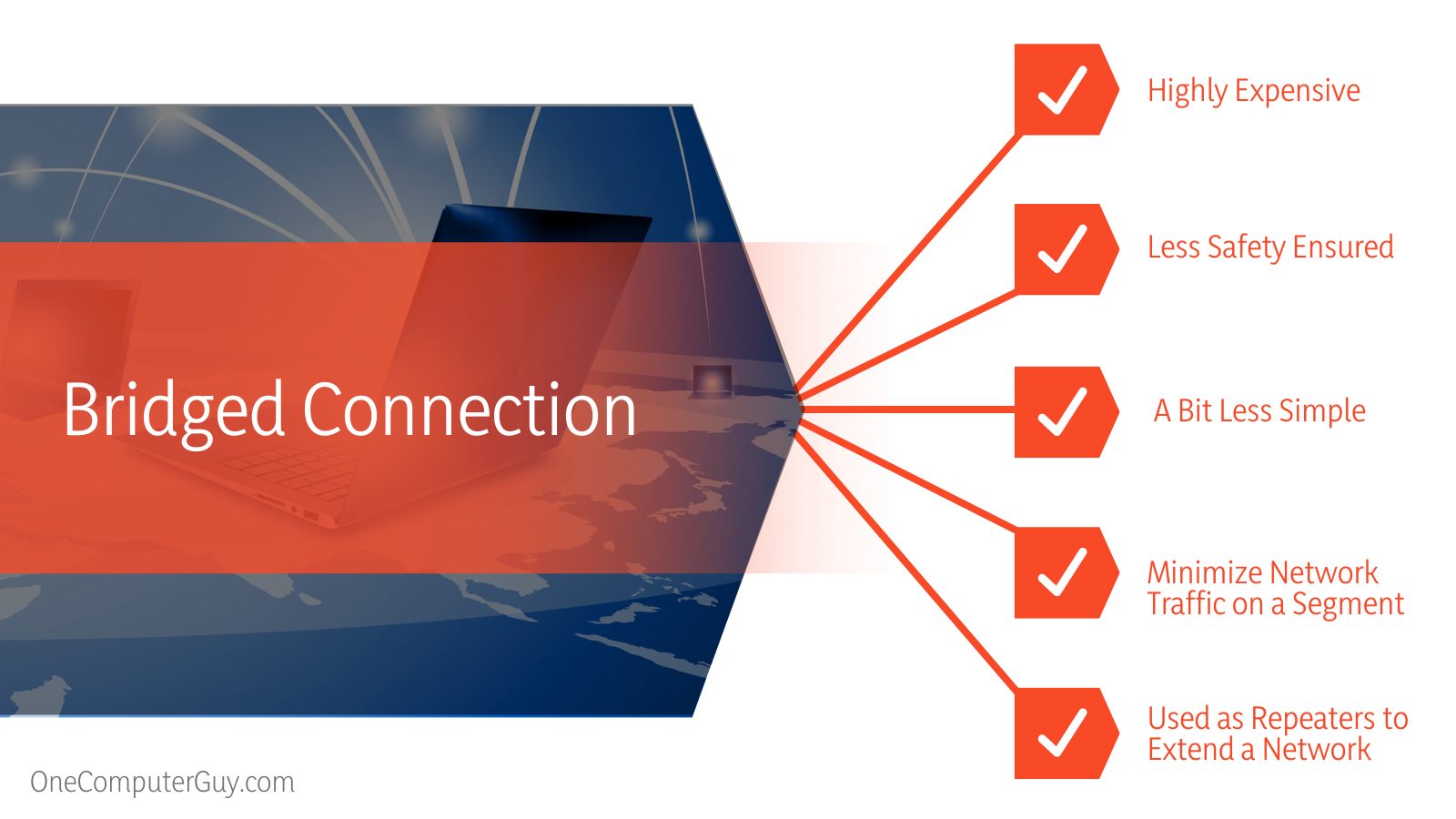
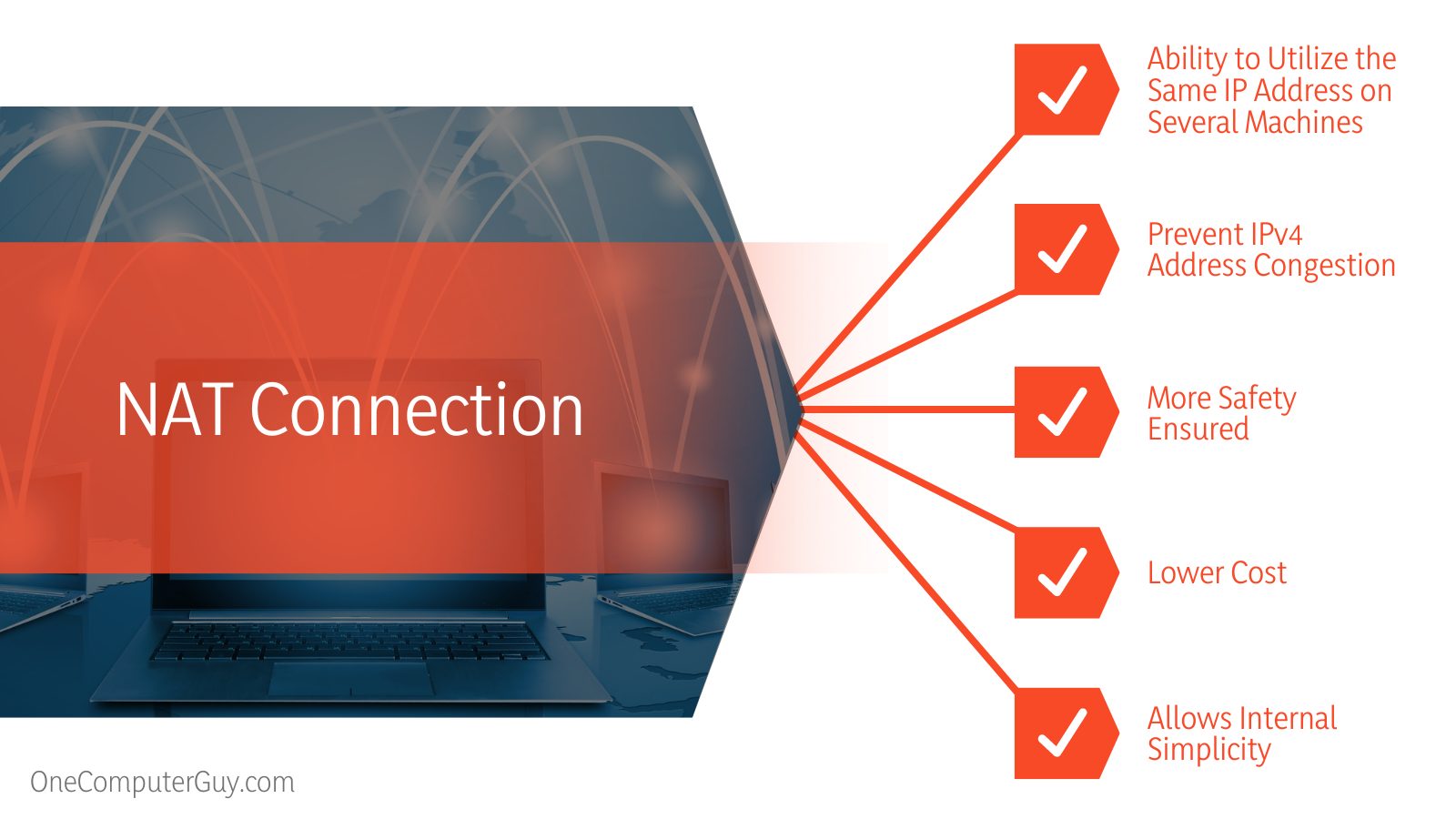
| More safety ensured | Less safety ensured |
| Lower Cost | Higher Cost |
| Allows internal simplicity | A bit less simple |
What Is The Difference Between NAT and Bridged?
The difference between bridged and nat computer networking mode is noticeable in four key areas: connection mode, IP Address, accessibility, and security. One of these criteria is significant to a different user, so it is critical to compare each other to determine which is the superior choice.
What Is NAT Connection Best For?
NAT (Network Address Translation) is best for people who want to use a single IP address for many devices as it doubles the security of its features and addresses translation in networking systems.
If all you want to do within the guest is surf the web, download files, and check email, this basic setting should be enough. However, when using Windows file sharing, keep in mind that there are some limits.
– What Is a NAT Connection Exactly?
Moreover, the nat connection is a hybrid of host only network to turn a single IP address space into a global one. This is used in conjunction with a router or firewall that connects two networks. With the help of a single public address, we may join several network address translations into an intranet.
This approach was created primarily to avoid addressing space exhaustion.
Nat is the simplest method of connecting a virtual machine to an external network, and it usually does not necessitate any network settings on both the host and guest systems.
– Outer and Inner Workings of NAT
The “outside” of the NAT is an external address that is normally routable, and the machines behind the NAT normally have a non-routable “interior” address. The NAT system in the middle makes a forwarding table entry consisting of (outside IP, outside port, nat host IP, nat host port, inside IP, inside port) when an inner address and an outside address are connected. The destination of any packet matching the first four parts is rewritten to the last two parts.
If a packet arrives that does not match an entry in the NAT table, the NAT box has no means of knowing where to send it unless a forwarding rule has been manually established. As a result, a system behind a NAT device is “protected” by default.
– NAT Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Nat’s primary benefit is that it can prevent IPv4 address congestion.
- Nat enables you to use your own private IPv4 addressing system, which prevents internal address changes if your service provider changes.
- When an enterprise uses NAT with its private IP address, they do not need to purchase a new IP address for each of their machines. They have the ability to utilize the same IP address on several machines. This will aid in the organization’s cost-cutting efforts.
- All of your original source and destination sources will be totally masked via In-Network Address Translation.
- Consistent network addressing is a scheme Nat uses.
Cons:
- Nat will evaluate the incoming and outgoing service data packets.
- It requires services like TCP or UDP.
- If a guest sends a request to a distant server, it will first check to see if the connection belongs to the NAT server.
- Hosts within the network may become unavailable at times.
Nat features a dedicated address space for using public IP addresses. This is because when the network grows, more IP addresses will be necessary. Nat helps avoid this congestion. More so, Without the user’s authorization, other hosts in the network cannot reach the hosts inside them. This demonstrates that they have increased security.
What Is Bridged Mode Best For?
A bridge network also increases the number of workstations attached and network segments. Bridging differs from routing. Routing makes multiple networks to communicate independently and remain separate.
 However, bridging links two different networks like they were a single network. Bridge also offers flexibility. Bridged can be used to connect networks with various designs. A bridged network makes network maintenance easier. Furthermore, by separating a LAN into tiny portions, network congestion can be decreased.
However, bridging links two different networks like they were a single network. Bridge also offers flexibility. Bridged can be used to connect networks with various designs. A bridged network makes network maintenance easier. Furthermore, by separating a LAN into tiny portions, network congestion can be decreased.
The device is called a wireless bridge if one or more portions of the bridged network are wireless.
– Bridged Mode Pros and Cons
Pros:
- By subdividing network communications, bridges can also minimize network traffic on a segment.
- Bridges are sometimes used as repeaters to extend a network.
- Only a few nodes share a collision domain in a network. Bridges boost bandwidth for these particular nodes.
- Connects similar network types with different cabling.
- Network dependability is good
Cons:
- A bridged network is a basic computer networking device that creates aggregate networks from multiple communication networks or segment networks.
- Creates a single aggregate network from multiple communication networks or network segments.
- Bridging is done on the data link layer of the OSI model (layer 2).
Frequently Asked Questions
– How Does The Bridged Connection Work?
The host shares its physical adapters with a “Bridged” network adapter, which means the adapter joins the network like any other physical system. This also necessitates that the adapter or Virtualbox has or receives a valid IP address from a DHCP server. The adapter is accessible from the network via bridged networking.
– How Does The NAT Connection Work?
NAT shares the host’s network connection by assigning a private network IP address to the router or Virtualbox nat and translating network requests from the guest. To the network, the host appears as a single system. By default, Virtual Machines using NAT networking cannot be accessible from other systems on the network.
– What Are The Differences Between Nat vs Bridged Mode With Regards to Connection?
All network activity will be masked as if it came from your Host-Only System in NAT mode. Your host will serve as a router (firewall), and your guests will be on their own private network. The Virtual Machine will be assigned to a separate subnet, just like your home network with a wireless router.
For example, if your host computer’s IP address is 192.168.6.1 and your Virtual Machine’s IP address is 192.168.6.3, your Virtual Machine can access the outside network like your host, but no outside access to your VM directly, it’s protected.
On the other hand, bridged mode duplicates another node on the physical network, and if DHCP is enabled on the network, your VM will get its IP address. Your Virtual Machine will be on a similar network as your host; for example, if your host’s IP address is 172.16.120.45, your Virtual Machine’s IP address will be 172.16.120.50. All computers on your host network can access it. Choose bridged networking if you want flexibility.
– Is Nat Preferable to Bridge?
This depends on what you are looking for in a networking system. There are several differences between the two connection modalities, each with its own set of advantages. If you want to save money and have to choose between nat and bridged networking, choose nat mode with the boundaries increased to cover the entire screen. As more resources are spent on each connection, bridged networking is more expensive to set up.
– When Should You Use Bridged Mode?
You should use bridged mode if you are connecting a second router to your network.
 – Is NAT Effective For Security Purposes?
– Is NAT Effective For Security Purposes?
Yes, NAT network configuration is most effective for security purposes. By masking the device’s IP address from the public network, NAT allows users to use the internet with more privacy and security, even while transmitting and receiving data. Users may restrict the highest number of concurrent NAT operations on a router and the number of NAT translations by using NAT rate-limiting.
– Is Bridged Mode Expensive?
It’s highly expensive, and we don’t recommend that you used it in every situation because of that. Furthermore, there’s no reason to use bridged mode if your home or business WiFi works well with good WiFi coverage and doesn’t frustrate you with sluggish speeds as you move farther away.
Bridged mode is the best option when you’re moving away from your router and need more WiFi coverage. It also allows devices on the private network to talk with one another without experiencing any performance difficulties. It is, however, quite costly to maintain.
– Is NAT A Simple Network?
Indeed, it is. It eliminates the need to renumber addresses when a network changes or merges. NAT also allows you to create an inside network virtual host to coordinate TCP load-balancing for internal network servers and hence, has more simplicity than bridged networking.
Conclusion
A bridge and nat network have extensive similarities and wide differences. In terms of seamless connection, the bridged mode is the best, since everything works as if it were a regular machine connected to that one. On the other hand, NAT allows you more security as your virtual machine is assigned to a different subnet.
In the end, we think that NAT is the best choice between the two after considering every variable possible. It’s less costly, more secure, and has internal simplicity, which is yet another positive detail about it.







